|

On eBay Now...
166 page Dental TOOTH RESTORATIVE IMPLANT PowerPoint Presentation on CD For Sale
When you click on links to various merchants on this site and make a purchase, this can result in this site earning a commission. Affiliate programs and affiliations include, but are not limited to, the eBay Partner Network.

166 page Dental TOOTH RESTORATIVE IMPLANT PowerPoint Presentation on CD :
$12.99
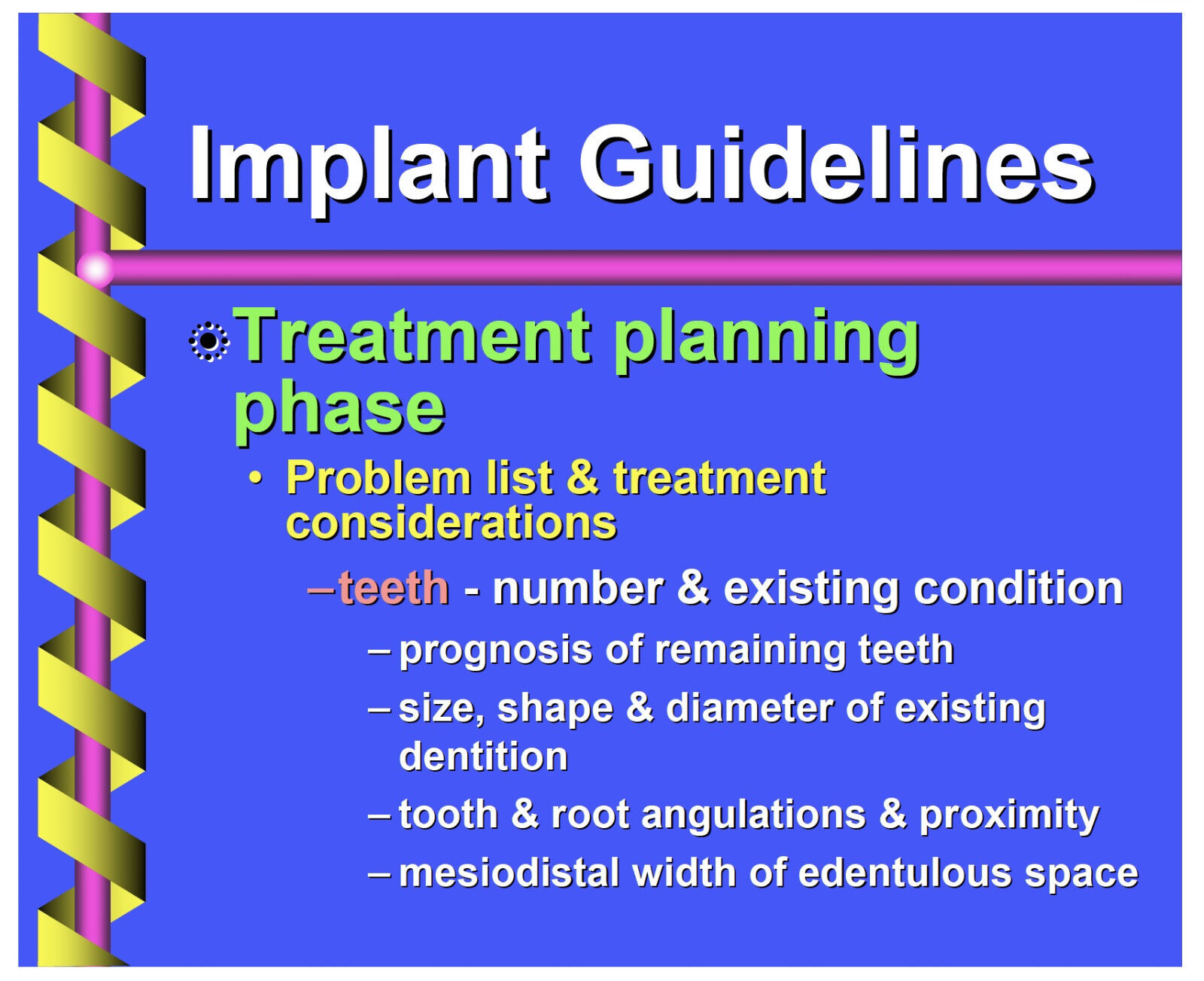
Thank you! If you do not wish to have your item(s) delivered on data disc(s), I can provide them on a flash drive and other means as well. Just let me know if a disc does not work for you and we can discuss delivery by other methods. COMBINING SHIPPING COSTS Are you purchasing multiple items? I will: a) combine all invoices before payment and charge shipping equivalent to one item, or b) refund all shipping costs in excess of one item after payment. All derivative (i.e. change in media; by compilation) work from this underlying U.S. Government public domain/public release data is COPYRIGHT © GOVPUBS $3.00 first class shipping in U.S. Includes the Adobe Acrobat Reader for reading and printing publications. Numerous illustrations and matrices. Contains the following key public domain (not copyrighted) U.S. Government publication(s) on one CD-ROM in both Microsoft PowerPoint and Adobe Acrobat PDF file formats: TITLE: Implant Guidelines for the Restorative Dentist, 166 pages SLIDE TOPICS, SUBTOPICS and CONTENTS: Implant Guidelines for the Restorative Dentist LCDR M.E. Berninghaus Comprehensive Dentistry NDS, Bethesda Implant Guidelines for the Restorative Dentist M.E. Berninghaus, DDS Comprehensive Dentistry Right now my life is just one learning experience after another…… By the end of the week I should be a genius! Jeanette Osias Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Definition an endosteal (within bone) alloplastic biologically compatible material surgically inserted into the edentulous bony ridge Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Use to serve as a foundation for prosthodontic restoration Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? History (endosseous) dates to Egyptians Greenfield (1913) - patented two-stage system Formiggini (1947) - “father of modern implantology” helical wire spiral Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? History (endosseous) single stage one-piece from bone through oral mucosa (crystal sapphire implants) two-stage bony implant separate from transmucosal portion variable design & materials Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Biomaterials most commonly used commercially pure (CP) titanium titanium-aluminum-vanadium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) - stronger & used w/ smaller diameter implants Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Titanium lightweight biocompatible corrosion resistant (dynamic inert oxide layer) strong & low-priced Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Fixture types HA coated Ti surface modified tap or self-tapping screw or press fit Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? “Osseointegration” Bränemark - late 1980’s direct structural & functional connection between ordered, living bone & surface of a load-carrying implant Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? “Osseointegration” similar soft-tissue relationship to natural dentition (sulcular epithelium) hemi-desmosome like structures connect epithelium to titanium surface Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? “Osseointegration” circumferential and perpendicular connective tissue no connective tissue insertion no intervening Sharpey’s fiber attachment Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? “Osseointegration” bone-implant interface osteoblasts in close proximity to interface separated from implant by thin amorphous proteoglycan layer osseointegration - highly predictable Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? “Osseointegration” bone-implant interface osteoblasts in close proximity to interface separated from implant by thin amorphous proteoglycan layer osseointegration - highly predictable Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? “Osseointegration” bone-implant interface oxide layer continues to grow- (2000 A at 6 yrs) - mineral ion interaction increase in trabecular pattern bone deposition & remodeling in response to stress Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? “Osseointegration” bone-implant interface oxide layer continues to grow- (2000 A at 6 yrs) - mineral ion interaction increase in trabecular pattern bone deposition & remodeling in response to stress Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Components & terminology coping or prosthesis screw (top) coping analog implant body abutment transfer coping (indirect or direct) Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Components & terminology hygiene screw abutment for screw, cement or attachment second stage permucosal abutment first stage cover screw implant body or fixture (bottom) Implant Guidelines Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types implants are small - standard abutment - usually 3.75mm or larger in diameter wide-body or wide-platform - up to 6.0mm Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types lengths - typically range from about 7 to 18mm Navy uses “external hex” good research literature able to be maintained (3i or Nobel Biocare systems) Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (Nobel Biocare) Fixtures Standard Mk II Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (Nobel Biocare) Abutments Standard CeraOne EsthetiCone MirusCone Angulated 17º (new) or 30º Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (Nobel Biocare) Standard no anti-rotational properties can use for multiple units can use for hybrid dentures Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (Nobel Biocare) CeraOne single tooth esthetic replacement abutment attached to fixture w/ restoration cemented to abutment accommodation for fixture misalignment can provisionalize Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (Nobel Biocare) EsthetiCone esthetic FPD restorations machined gold cylinder abutment allows crown margin to seat close to fixture (within 1mm) Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (Nobel Biocare) MirusCone esthetic FPD restorations use when decreased vertical height allows 4.5mm clearance Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (Nobel Biocare) Angulated abutment 17º or 30º use to achieve better esthetic result where complicated anatomy exists use if less than ideal fixture placement use where esthetic cervical margin required Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (Nobel Biocare) CeraOne EsthetiCone MirusCone Angulated abutments All come with narrow, regular or wide platforms (NP, RP, WP) Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (3i) Fixtures MicroMiniplant Miniplant Standard Wide Diameter ( surface area to use where vertical height) Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (3i) Fixtures ICE (incremental cutting edge) super self-tapping implant uses tapered cutting flutes allows more placement control rapid bone engagement & implant stabilization Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (3i) Abutments EP (conical) - (esthetic profile) Gold UCLA-type Two-piece abutment post STA (standard) Pre-Angled New Gold Standard ZR (zero rotation) Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (3i) Gold UCLA-type abutment screw-retained at fixture level non-segmented abutment screw-retained crown to implant uses larger screw because it runs all the way to the fixture Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (3i) Gold UCLA-type abutment thin buccal-lingual tissues limited inter-occlusal distance (as little as 4.5mm) single or multiple units Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (3i) EP (conical) - (esthetic profile) screw-retained crown to the abutment gold cylinder non-parallel implant placement single or multiple units minimum 7mm inter-occlusal distance required Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Modern types (3i) Two-piece abutment post non-rotational cement-retained crown to the abutment simplicity of treatment - chairside preparation use when access to posterior region w/ screw driver is limited Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? What’s new? (3i) Prep-Tite Posts screw retained abutment standard impression procedure cemented restoration 6º taper with 3 vertical grooves multiple collar heights Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? What’s new? (3i) Osseotite (“clot retentive surface”) specific micro-topographic acid-etched implant surface design Vs. machined-surface implant single stage implant loaded after 2 months claim 98.5% success after 3 years Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Remember…. For FPD’s plan for screw-retained restorations no anti-rotational properties always use at least 2 fixtures when restoring posterior spaces not bound by natural teeth! Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Advantages no preparation of tooth/adjacent teeth bone stabilization & maintenance retrievability improvement of function psychological improvement Implant Guidelines What is a dental implant? Disadvantages risk of screw loosening risk of fixture failure length of treatment time need for multiple surgeries challenging esthetics Implant Guidelines Consultation Appointment Treatment planning phase “Diagnosis begins with a complete patient evaluation” guidelines for “decision-making” process treat the “entire” patient restore form, function & esthetics Implant Guidelines Consultation Appointment Treatment planning phase problem list & patient desires initial evaluation chief complaint medical/dental history review intra/extraoral exam evaluation of existing prosthesis Implant Guidelines Consultation Appointment Treatment planning phase initial evaluation diagnostic impressions/articulated casts radiographs - panoramic and periapical (CT scan or tomography - as indicated) photographs Implant Guidelines Consultation Appointment Treatment planning phase treatment options/informed consent explanation of long-term commitment restorative - surgical joint consult two-stage surgery stage I stage II Implant Guidelines Consultation Appointment Treatment planning phase two-stage surgery (use of clear acrylic surgical stent is mandatory!) stage I - implant fixture placement w/ cover screw (left submerged) Implant Guidelines Consultation Appointment Treatment planning phase stage I - healing phase 3 month minimum (mandible ) - usually 6 months for posterior regions 6 month minimum (maxilla) - usually 6-9 months for all regions Implant Guidelines Consultation Appointment Treatment planning phase stage II - uncovering & placement of transmucosal healing abutment healing phase 4-6 weeks for soft tissue healing Implant Guidelines Consultation Appointment Treatment planning phase restorative phase maintenance and regular recall fee & payment policy goal to restore form, function & esthetics Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth periodontium radiographic analysis surgical analysis esthetic analysis Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis advs/disadvs of proposed treatment referrals/specialty consults appointment sequencing treatment alternatives Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth periodontium radiographic analysis surgical analysis esthetic analysis Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth - number & existing condition prognosis of remaining teeth size, shape & diameter of existing dentition tooth & root angulations & proximity mesiodistal width of edentulous space Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth - number & existing condition minimum 6-7mm between teeth to facilitate implant placement (based on 3mm fixture) > 1.5mm between implant & natural teeth 7mm from center of implant - to center of implant for edentulous area Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth - number & existing condition more than 10mm mesiodistal space - single tooth implant not recommended (multiple abutments should be splinted) Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth periodontium radiographic analysis surgical analysis esthetic analysis Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations periodontium - bone support Lekholm & Zarb classification quality - best - thick compact cortical bone w/core of dense trabecular cancellous bone best region - mandibular symphysis; poorest in posterior regions Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations periodontium - bone support quantity - required for implant - 6mm buccal-lingual width w/sufficient tissue volume 8mm interradicular bone width 10mm alveolar bone above IAN canal or below maxillary sinus Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations periodontium - bone support quantity - required for implant - if inadequate bone support may need ridge or site augmentation ramus or chin graft (autograft) DFDBA (allograft) Bio-Oss(xenograft) Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations periodontium - bone support place implants minimum of 2mm from IAN canal or below maxillary sinus crown/root ratio mobility furcations probing depths Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations periodontium mucogingival problems need sufficient tissue volume to recreate gingival papilla need some attached gingiva to maintain peri-implant sulcus 1st year post-op bone resorption ~ 1mm *crest of bone optimal 2- 3mm below CEJ Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations periodontium mucogingival problems place implant 2-3mm apical to free gingival margin of adjacent tooth recreates biologic width of peri-implant sulcus *soft tissue height < 2mm or > 4mm may create challenge! Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations periodontium oral hygiene - important pre & post systemic manifestations - ie. diabetics are predisposed to delayed healing destructive habits - smoking is contraindicated - delayed or inadequate tissue healing & osseointegration noted Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth periodontium radiographic analysis surgical analysis esthetic analysis Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations radiographic analysis periapical pathology radiopaque/radiolucent regions adequate vertical bone height adequate space above IAN or below maxillary sinus Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations radiographic analysis adequate interradicular area bone quality & quantity radiographs - panoramic and periapical (CT scan or tomography - as indicated) Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations radiographic analysis radiographs - aid to determine amount of “space”& bone available CT (computed tomography) scan - gives more accurate & reliable assessment of bone (quality, quantity & width) & locale of anatomic structures Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations radiographic analysis - radiographic stent - (can double as surgical stent) acrylic stent with lead beads or ball -bearings (5mm) placed in proposed fixture locations allows more accurate radiographic interpretation Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations radiographic analysis - distortion (common to all X-rays) Panorex ~ 25% vertical; horizontal varies w/ head position (1.20-1.25x) CT ~ 1:1; 1-2mm vertical error; *most accurate (1.0-1.1x) Lateral Ceph ~ 8% Periapical ~ 2.5-5% Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth periodontium radiographic analysis surgical analysis esthetic analysis Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations surgical analysis - surgical guide stent - *one of the most critical factors for obtaining an ideal surgical & esthetic result used during fixture installation as guide for optimal B/L and M/D position use of buccal channel drill guide allows improved access & visibility Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations surgical analysis - implant length/diameter determined by quantity of bone apical to extraction site use longest implant safely possible diameter dictated by corresponding root anatomy at crest of bone Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations surgical analysis treatment options immediate - place implant at time of tooth extraction delayed immediate - 8-10 week delay delayed - 9-10 months or longer immediate will not allow bone resorption, but delayed allows bone fill for stabilization Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations surgical analysis proper surgical technique during implant placement is critical minimal heat generation important < 47º Celsius for one minute or less provides most predictable healing response Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations teeth periodontium radiographic analysis surgical analysis esthetic analysis Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations esthetic analysis smile line - high in maxilla; low in mandible lip shape - full Vs. thin existing ridge defect - if visible w/ high smile line will need augmentation Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations esthetic analysis implant emergence profile (360º) restored implant should appear to “grow” or emerge from the gingiva very natural & desirable in appearance avoid “tomato on a stick” crowns or periodontal problems may develop Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis advs/disadvs of proposed treatment referrals/specialty consults appointment sequencing treatment alternatives Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis improvement of function and/or esthetics (?) parafunctional habits can be destructive teeth lost to occlusal trauma or parafunction - less success w/ implants Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis diagnostic casts (mounted to determine opposing occlusion) ridge width existing inter-arch vertical space 14-15mm minimum for complete denture; partially edentulous varies by implant type Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis maxillo-mandibular relations jaw classifications Class II may have greatest benefit Class III requires surgical intervention Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis advs/disadvs of proposed treatment referrals/specialty consults appointment sequencing treatment alternatives Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations advs/disadvs of proposed treatment are as individual as the case being treatment planned! cost patient desires clinician abilities etc. Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis advs/disadvs of proposed treatment referrals/specialty consults appointment sequencing treatment alternatives Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations referrals/specialty consults can prognosis be improved with (?): orthodontics periodontal therapy endodontic therapy Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations referrals/specialty consults pre-prosthetic surgery extractions ridge contouring or exostosis removal osteotomy bone or soft tissue augmentation Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis advs/disadvs of proposed treatment referrals/specialty consults appointment sequencing treatment alternatives Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations appointment sequencing length of treatment time need for multiple surgeries Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations occlusal analysis advs/disadvs of proposed treatment referrals/specialty consults appointment sequencing treatment alternatives Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Problem list & treatment considerations treatment alternatives fixed partial dentures removable partial dentures resin-bonded fixed partial dentures orthodontics do nothing! Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Indications good general health adequate bone quality & volume appropriate occlusion & jaw relations inability to wear conventional prosthesis unfavorable number/location of abutment single tooth loss Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Contraindications unrealistic patient expectations alcohol/drug dependence (smoking) parafunctional habits psychological factors anatomical factors inadequate ridge/interarch dimensions immunosuppression Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase Contraindications (relative) (need surgical intervention) ramus graft inadequate bone at implant site excessive bony concavities sinus lift or IAN transposition inadequate vertical space for implant Implant Guidelines Treatment planning phase “Osseointegrated implants can be placed in the irradiated mandibles of selected patients without hyperbaric oxygen treatment” Niini, Ueda, Keller, Worthington; Experience with Osseointegrated Implants Placed in Irradiated Tissues in Japan and the United States, Intl J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1998; 13:407-411 Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success Maintenance and Recall Hygiene Aids Problems Implant Guidelines Maintenance Primary goal is to protect and maintain “tissue-integration”; good oral hygiene is a key element! Implant Guidelines Maintenance “Implant patients should be thoroughly instructed in maintenance therapy with the understanding that the patient serves as co-therapist” Grant et al, Periodontics, in the Tradition of Gottlieb and Orban, ed 6. St. Louis, CV Mosby Co, 1988, pp1075-1094. Implant Guidelines Maintenance “Any practitioner wishing to practice dental implantology must be knowledgeable concerning postinsertion maintenance of the implant” 1988 National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success Maintenance and Recall Hygiene Aids Problems Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success: (most important is good diagnosis!) no peri-implantitis no associated radiographic radiolucency marginal bone loss 1.0-1.5mm first year; then < 0.1mm annually thereafter Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success: tissue integration: bone/soft tissue “osseointegration” absence of mobility no progressive soft tissue changes or bone loss stable clinical attachment level Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success: absence of bleeding upon probing/excessive probing depths absence of discomfort success rate varies with bone quality, loading dynamics, etc. Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success: anticipated success rate of +97% anterior mandible; 90% maxilla; decreases in posterior quadrants due to poorer bone quality (10 yrs) best bone: good cortical with some cancellous for vascular supply Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success Maintenance and Recall Hygiene Aids Problems Implant Guidelines Maintenance Maintenance & Recall: Four elements home-care regimen periodic recalls reinforcing regimen strict adherence to recall schedule & verification of function, comfort, and esthetics lifetime maintenance commitment Implant Guidelines Maintenance Maintenance & Recall: Frequency of recall immediate post-delivery 24 hours one week two weeks (re-torque if needed) 6 months bi-annual or annual evaluation Implant Guidelines Maintenance Maintenance & Recall: Clinical Parameters of Evaluation oral hygiene including plaque index implant stability (evaluate mobility) retrievability peri-implant tissue health crevicular probing depths Implant Guidelines Maintenance Maintenance & Recall: Clinical Parameters of Evaluation bleeding radiographic assessment (serial) crestal bone level & integrity of attachment systems proper torque on screw joints occlusion Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation oral hygiene (plaque index) plaque is 1º etiologic factor in tissue destruction (peri-implant and natural tooth) review oral hygiene instruction monitor through plaque indices same requirements as for natural teeth use neutral sodium fluorides Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation implant stability (evaluate mobility) may be the key indicator of fixture health minimal mobility w/ osseointegrated fixtures: 17- 57um buccal;17- 66um lingual) no significant difference in osseointegrated fixture mobility relative to fixture length (Sekine et al) implants may sustain extensive bone loss w/o inc mobility if critical amount bone left Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation retrievability failing implant may be masked if connected to same prosthesis important to remove FPD to evaluate annual removal recommended for multiple-unit prosthesis early failure detection will minimize fibrous tissue zone size & may allow placement of wider diameter fixture Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation peri-implant tissue health visual inspection: signs of pathoses? Alterations in color, contour & consistency alveolar mucosa may surround implant & appear more erythematous than gingiva tissue movement when adjacent tissues retracted may affect soft-tissue-implant attachment ~ (detrimental) perimucosal keratinized tissue is best Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation crevicular probing depths most accurate means of detecting peri-implant destruction (use plastic probes) probing measurements closely approximate actual bone levels avoid during first 3 months after abutment connection to avoid damaging weak epithelial attachment may be difficult if threads supra-osseous Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation bleeding controversy as to significance of BOP at peri-implant interface BOP may precede clinical signs of inflammation BOP & radiographic changes are most valid indicators of peri-implant breakdown recommend continued use of peri-implant sulcus probing to monitor implant success Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation radiographic assessment one of most valuable measures of implant success of value when cannot probe area due to constricted implant neck, and to assess future mobility without FPD removal to accurately determine amount of bone loss in absence of increased crevicular depth Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation radiographic assessment compare bony changes with stable landmarks - implant threads - (one-half thread = 0.3mm) compare horizontal/vertical implant dimensions between serial radiographs periapical radiographs = 2.5 - 5% image magnification Vs. direct clinical measurements Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation radiographic assessment bone level determination should be based only upon standardized periapical radiographs threads of implant must appear sharp & well-delineated on X-ray to be accurate X-ray beam: direct 9º from line perpendicular to long axis of implant keep film parallel & close to implant Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation radiographic assessment recommend kVp of not < 60 (best 65-70) exposure time determined so internal mechanical structure of fixture is clearly visible use long-cone paralleling technique w/ paralleling film holder can use intra-oral landmarks and film holder to standardize horizontal angulation Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation radiographic assessment quality in film development is paramount!!! post-op radiographic intervals: not between fixture placement to abutment connection one week after abutment insertion immediately following fixed prosthesis insertion, then 6 months later annually for first 3 years, then every 2 years Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation radiographic assessment expect 1.0mm marginal bone loss during first year postinsertion; 0.1mm per year anticipated thereafter greater bone loss observed in maxilla Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation radiographic assessment rapid bone loss seen if: fractured fixture initial osseous trauma at insertion fixture over-tightening occlusal trauma poor adaptation of prosthesis to abutment “normal” physiologic response plaque-associated infection (peri-implantitis) Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation radiographic assessment REMEMBER ……… Endosseous implants may lose extensive amounts of bone support without showing rather obvious radiographic changes or increase in mobility detectable in periodontally involved teeth !!! Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation proper torque on screw joints loosened screws are the most common problem can result in localized inflammation, loose restorations, and discomfort if re-torquing a loose abutment - care not to strip or “round-off” the hex excessive force can fracture screw/implant or create increased stresses in the bone Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation occlusion excessive force concentrations - result in extensive bone loss and implant fracture MAJOR CAUSE: poor abutment prosthesis adaptation poor force distribution & improperly planned occlusal schemes also factors recommend anterior guidance ** BEST group function/balanced occlusion also Implant Guidelines Clinical Parameters of Evaluation occlusion goal to prevent lateral forces on posterior implants concentrated in cervical area relationship between parafunctional activity & increased marginal bone loss ideal is “light centric” occlusion only; no contact in lateral excursions no contact in MI, but with hard clench will hold shim stock (.0001”) Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success Maintenance and Recall Hygiene Aids Problems Implant Guidelines Maintenance Hygiene Aids: plastic scalers - ONLY! - for abutment scaling to prevent easy abrasion of soft titanium; use in only one direction starting at the gingiva (best are from 3i) ultrasonic scalers - NO! - do not use Titan-S or ultrasonic scalers unless special non-metal tips used Implant Guidelines Maintenance Hygiene Aids: prophy jets - use with caution! fine prophy paste or flour of pumice - OK! - use with blue rubber tips or rubber prophy cups Super-Floss or Post-care - nylon fibers - thread for interproximal use between abutments and under extensions Implant Guidelines Maintenance Hygiene Aids: end-tufted & small interdental brushes (Proxibrushes) - for cleaning buccal & lingual abutment surfaces; all metal surfaces must be nylon coated electric toothbrushes - use at discretion of dentist; may be useful if limited manual dexterity Implant Guidelines Maintenance Hygiene Aids: chlorhexidine - use during peri-surgical periods or as needed if episodes of acute soft tissue inflammation occur fluoride rinses or gels - use neutral sodium fluoride to avoid damage to titanium fixtures that may occur with acidulated types Implant Guidelines Maintenance Criteria for success Maintenance and Recall Hygiene Aids Problems Implant Guidelines Maintenance Problems: soft tissue reactions fractured or loosened screws failing or failed fixture broken attachments/ components Implant Guidelines Problems: soft tissue reactions most common due to loose screws poor oral hygiene can lead to “peri-implantitis” - may result in progressive bone loss lack of attached periabutment soft tissue failed or failing implants Implant Guidelines Problems: soft tissue reactions treatment: remove offending screw, tighten abutment & reinsert prosthesis reinforce oral hygiene soft-tissue autograft replacement of failed implant Implant Guidelines Problems: fractured or loosened screws 1st suspicion when complaint of “loose” implant or discomfort use correct screwdriver for screw head without excess force or can “round off” hex if retrieving (“teasing out”) fractured screw caution not to damage hex Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture failing implant Vs failed implant “implantitis” Vs periodontal disease Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture failing implant clinical signs: progressive crestal bone loss; soft tissue pocketing; BOP w/ possible purulence; tenderness to percussion or torque Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture fixture loss failing implant causes: surgical compromises (bone overheating, lack of initial stability); nonpassive superstructures; too rapid initial loading; functional overload; inadequate screw joint closure; infection Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture fixture loss failing implant treatment: remove and replace with larger diameter fixture; or treat infection & re- evaluate interim - remove prosthesis & abutments & irrigate area w/ CHX; disinfect components & reinsert Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture fixture loss failed implant clinical signs: mobility; “dull” percussion sound; peri-implant radiolucency (connective tissue implant encapsulation may not be visible on radiograph) Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture fixture loss failed implant (most noted at Stage II) causes: surgical compromises (bone overheating, lack of initial stability); nonpassive superstructures; too rapid initial loading; functional overload; inadequate screw joint closure; infection Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture fixture loss failed implant (most noted at Stage II) treatment: removal of implant Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture fixture loss “implantitis” Vs periodontitis clinical signs:similar clinical presentation w/ same pathogenic microorganisms causes:poor oral hygiene; bacteria; cause may be unknown (?) Implant Guidelines Problems: failing or failed fixture fixture loss “implantitis” Vs periodontitis treatment: consults to provider - consider remake or guided tissue regeneration, etc. interim - remove prosthesis & abutments & irrigate area w/ CHX; disinfect components & reinsert Implant Guidelines Problems: broken attachments/ components remove offending attachment (if possible) and replace or provisionalize be careful not to damage external hex or scratch titanium fixture or abutment Implant Guidelines Case Selection Implant recommended replacement of teeth #27,19 & 30 Implant not recommended replacement of tooth #28s Case #1 Implant Guidelines Implant recommended 46 y/o male presented with failing NSRCT #27 and severe localized periodontitis tooth deemed hopeless and extracted Implant Guidelines Implant recommended 4.0 x 18mm Nobelpharma fixture placed Implant Guidelines Implant recommended Cera-One abutment restored with cemented (Ketac Cem) PFM crown Case # 2 Implant Guidelines Implant recommended 31 y/o female presented with missing #19 & 30, and retained #17 & 32 (third molars) Implant Guidelines Implant recommended mesial-angulated #18 & 31 with inadequate mesial-distal and interarch spacing due to super-erupted opposing # 3 & 14 Implant Guidelines Implant recommended buccal-lingual ridge widths in areas of missing #19 and #30 also deficient Implant Guidelines Implant recommended teeth # 17 & 32 extracted and bilateral ramus grafts placed at edentulous sites (#19 & 30) Implant Guidelines Implant recommended molar uprighting of teeth #18 & 31 completed to create adequate space for implants Implant Guidelines Implant recommended 5.0 x 11.5mm 3i fixtures placed bilaterally Implant Guidelines Implant recommended restoration of fixtures with screw-retained non-segmented UCLA abutments w/ PFM crowns Implant Guidelines Implant recommended restoration of teeth # 3 & 14 with PFM crowns to re-establish proper occlusal plane Case # 3 Implant Guidelines Implant not recommended 34 y/o male presented with past history of supernumerary #28 Note: dilacerated root to mesial on #28 Implant Guidelines Implant not recommended edentulous site presented with inadequate facial bone, and inadequate spacing existed between #27 & 28 root apices to allow implant placement Implant Guidelines Implant not recommended after two years of orthodontic therapy, #28 failed to move to facilitate implant placement Implant Guidelines Implant not recommended edentulous area restored with a resin-bonded fixed partial denture (RBFPD #27-28) QUESTIONS ??? USS BRIDGE


AVENGERS #166 CGC 9.6 WHITE PAGES // MARVEL COMICS 1977 $115.00

166 Page AAF Italy Luftwaffe Surrender V-1 V-2 Rocket Jet Documents on Data CD $14.99

Thor #166 Him/Adam Warlock, Low Grade, Masthead/ Top Of First Page Torn Off,1969 $19.99

4,166 Page U.S. Army War Department Intelligence Bulletins 1942-1945 on Data CD $14.99

Uncanny X-Men #166 CGC 9.4 1st Appearance of Lockheed White Pages; 1983 $39.99

166 Page Naval Aviation PREFLIGHT AIRCRAFT ENGINES And SYSTEMS Manual on CD $12.99

Once Our Land - Omnibus Trade Paperback - Page 166 - Black - Comic Printer Plate $69.99

166 page FM 34-25 CORPS Intelligence Electronic Warfare Operations Manual on CD $14.99
|